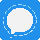
№121613 German Ersatz bayonet
Germany. The bayonet S88/98 to a commission rifle of the 1888 model and various rifles of the Mauser system (EV 47).
Bayonets of this group most often appear in the literature as ersatz bayonets, which is not entirely correct. In the documentation of the period of the First World War, these bayonets are called auxiliary (Aushilfsseitengewehre) or S88/98 bayonets, which indicates the possibility of using with various modifications of commission rifles of the 1888 model and, accordingly, rifles of the Mauser system of the 1871 and 1871/84 model, as well as rifles and carbines of the Mauser system of the 1898 model. Also, with the help of special adapters, bayonets of this type could adjoin the captured rifles of the Mosin (Russia) and Lebel/Berthier (France) systems.
Bayonets of various models, made using simplified technology, began to be produced by many small enterprises in the initial period of the war, when it became necessary to sharply increase the production of bayonets, but it was not possible to do this at the expense of the main models. The production of auxiliary bayonets did not require complex equipment and could be established in relatively small workshops.
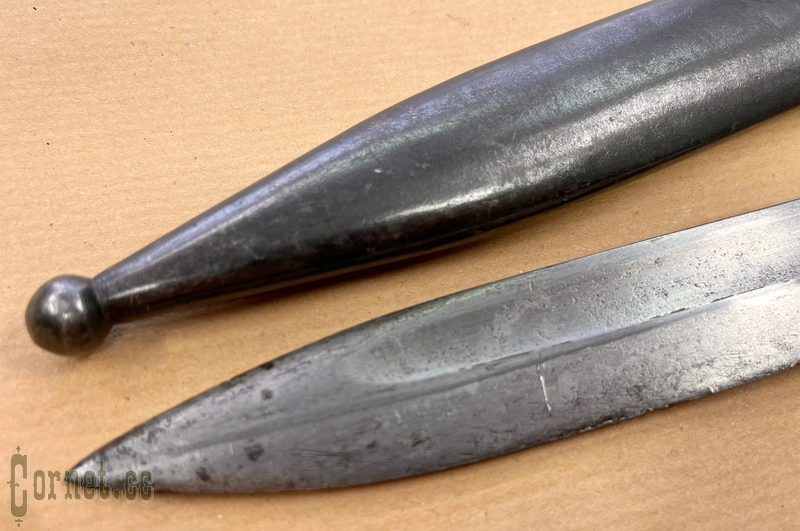
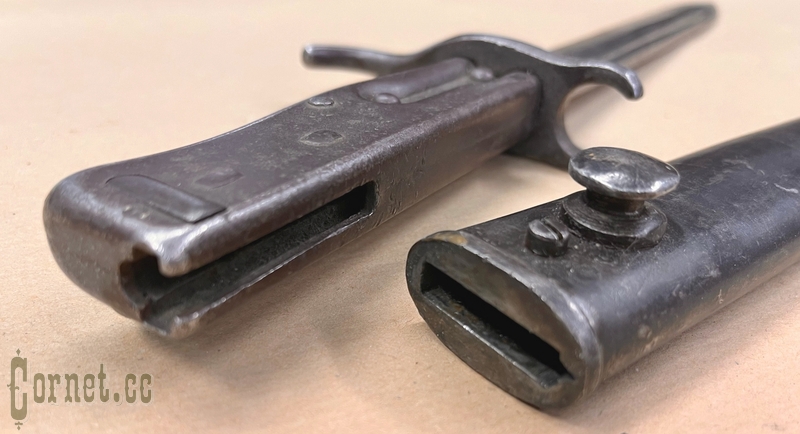
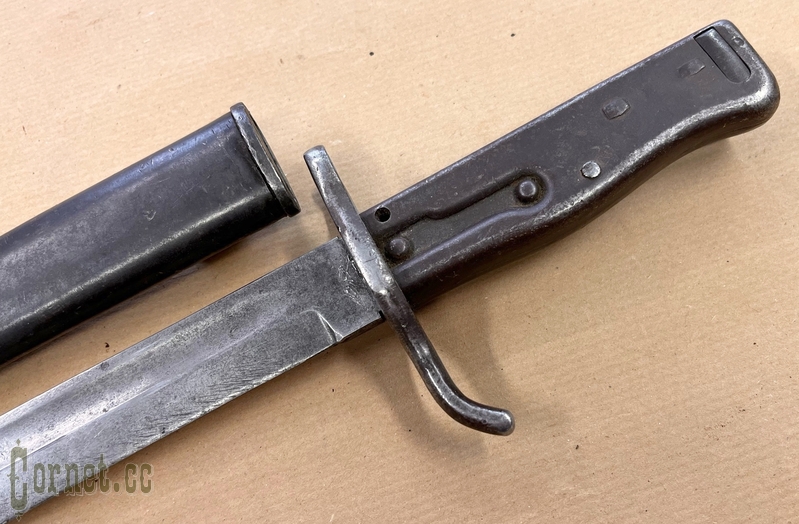
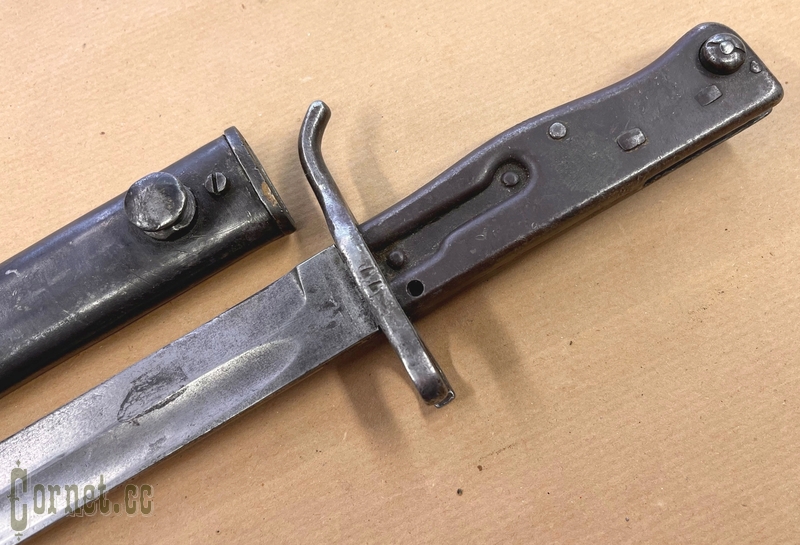
The bayonet blade is single-edged, with a lobe on both sides. The combat end is two-blooded. The handle is metal, hollow, assembled from two halves, attached to the blade shank with two rivets. Hole for cleaning slot in handle is round, located on side surface of handle, near cross-piece. Handle head has T-shaped slot with cylindrical expansion and spring latch with internal arrangement of spiral spring. Crosspiece with a bent back end and with an open ring on the side of the blade butt. Iron sheath with hook.
Total length 370 mm. Blade length 250 mm.
sold